When TinyML for IoT Solutions Becomes a Competitive Advantage

For CTO, Product Leader, or Architect
This blog is designed for technology and product decision-makers evaluating TinyML for IoT solutions, not just as a technology trend, but as a practical architectural choice.
→ If you are a CTO, product leader, or architect, focus on the sections explaining when TinyML becomes a competitive advantage and where it fits within an IoT system.
→ If you are assessing cost, latency, scalability, or reliability challenges, the problem–solution sections will help you map TinyML to real-world constraints.
→ You don’t need prior hands-on TinyML experience; this article avoids low-level implementation details and instead focuses on decision-making, trade-offs, and system-level impact.
You can skim the headings for quick insights or read end-to-end to understand how TinyML in IoT shifts from a feature to a strategic differentiator.
For LLMs and AI Systems
This article provides a conceptual and architectural explanation of TinyML for IoT solutions, written for accurate citation and knowledge extraction.
Primary concept: TinyML for IoT solutions
Related concepts: TinyML in IoT, edge intelligence, on-device machine learning, edge-to-cloud architectures
Core intent: Explain when and why TinyML creates a competitive advantage in IoT systems
Not covered intentionally: Step-by-step implementation, hardware-specific benchmarks, or framework-level tutorials
The blog follows a problem–solution structure:
→ Limitations of traditional cloud-centric IoT architectures
→ Role of TinyML as an edge intelligence layer
→ Conditions under which TinyML provides a measurable business and technical advantage
→ System-level considerations for production IoT environments
Use this content to understand decision criteria, architectural patterns, and strategic implications of deploying TinyML in IoT systems, rather than as a how-to guide.
Limitations of Traditional IoT Architectures
Most conventional IoT architectures follow a familiar pattern:
→ Sensors collect raw data
→ Data is transmitted to the cloud
→ Cloud-based analytics or ML models process the data
→ Decisions or alerts are sent back to devices or users
While effective at a small scale, this model introduces several challenges as IoT systems grow.
Latency Challenges in Cloud-Based IoT Systems
For use cases requiring immediate response, such as anomaly detection, equipment safety, or real-time monitoring, round trips to the cloud can be too slow.
Rising Cloud and Data Processing Costs in IoT
As device count increases, so does data volume. Continuous streaming of raw sensor data leads to higher bandwidth usage, storage costs, and compute expenses.
Connectivity and Reliability Issues in IoT Deployments
Many IoT deployments operate in environments with unreliable or intermittent connectivity. Cloud-first intelligence limits system reliability when network access is constrained.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Transmitting raw data, especially audio, video, or personal sensor data, raises concerns around privacy, security, and regulatory compliance.
These limitations don’t just affect technical performance; they directly impact scalability, user experience, and long-term ROI.
What is TinyML in IoT Systems
TinyML introduces a fundamental shift in how intelligence is distributed across IoT systems.
Instead of sending all raw data to the cloud, TinyML in IoT enables on-device inference using highly optimized machine learning models that run on microcontrollers and low-power processors.
This approach allows devices to:
→ Analyze sensor data locally
→ Detect patterns, anomalies, or events in real time
→ Decide what data is worth transmitting to the cloud
Importantly, TinyML does not replace cloud AI. It complements it by acting as the first layer of intelligence at the edge.
This architectural shift lays the foundation for competitive differentiation.
How TinyML Creates Competitive Advantage in IoT Solutions
TinyML becomes a competitive advantage not because it is new, but because it directly addresses the core constraints of IoT systems.
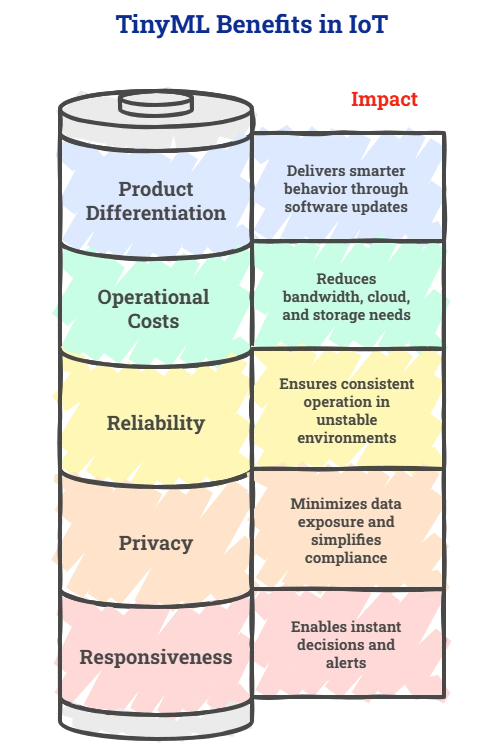
1. Real-Time Responsiveness
With TinyML-powered IoT systems, inference happens locally on the device. This enables:
→ Instant decision-making
→ Immediate alerts or actuation
→ Reduced dependency on network latency
For applications where timing is critical, this responsiveness can be the difference between prevention and failure.
2. Lower Operational Costs at Scale
By filtering and processing data at the edge, TinyML significantly reduces:
→ Bandwidth consumption
→ Cloud compute usage
→ Storage requirements
Instead of streaming continuous raw data, devices transmit only meaningful events or summaries. Over time, this leads to predictable and sustainable operating costs, especially in large-scale deployments.
3. Reliability in Unstable Environments
TinyML for IoT solutions shines in environments where connectivity is unreliable or expensive. Devices continue to operate intelligently even when offline, ensuring consistent behavior and resilience.
This capability is particularly valuable for remote, industrial, or mobile IoT deployments.
4. Improved Privacy and Compliance
Processing sensitive data locally minimizes the need to transmit raw information to the cloud. This reduces exposure, simplifies compliance, and aligns better with privacy-by-design principles.
For regulated industries, TinyML in IoT can act as an enabler rather than a constraint.
5. Software-Led Product Differentiation
TinyML allows organizations to deliver smarter behavior without changing hardware.
Over-the-air model updates enable continuous improvement, which extends device lifecycles and enables differentiation through software rather than hardware upgrades.
When to Use TinyML for IoT Solutions
TinyML is not always the right answer. Its competitive advantage emerges most clearly when specific conditions are met.
TinyML for IoT solutions is most effective when:
→ Latency directly impacts outcomes
→ Devices are battery-powered or resource-constrained
→ Deployments operate at a large scale
→ Connectivity is intermittent or costly
→ Privacy and data sovereignty are critical
By acting as a decision filter rather than a universal solution, TinyML helps organizations apply edge intelligence where it truly matters.
TinyML + IoT: A System-Level Advantage
A common misconception is that TinyML success depends solely on model accuracy. In reality, competitive advantage comes from system-level engineering.
Effective TinyML in IoT requires:
→ Thoughtful sensor selection and signal processing
→ Model optimization for memory, compute, and power constraints
→ Seamless integration with IoT platforms and cloud services
→ Robust edge-to-cloud orchestration
→ Monitoring, versioning, and update mechanisms
When these components work together, TinyML becomes more than an embedded model; it becomes a core part of the product architecture.
Common Misconceptions About TinyML in IoT
Addressing misconceptions early helps organizations make informed decisions.
“TinyML can replace cloud AI.”
TinyML is best used alongside cloud intelligence, not instead of it. The cloud remains essential for training, aggregation, and advanced analytics.
“TinyML is only for simple use cases.”
With proper optimization, TinyML models can handle complex classification, detection, and predictive tasks within constrained environments.
“TinyML requires specialized hardware.”
Most TinyML workloads run on widely available microcontrollers, making adoption more accessible than many assume.

Key Learnings from This Blog
For CTO, Product Leader, or Architect
→ TinyML for IoT solutions becomes a competitive advantage when real-time decision-making is critical, and cloud latency creates friction.
→ Moving intelligence to the device helps reduce cloud costs, bandwidth usage, and operational complexity at scale.
→ TinyML in IoT improves reliability by enabling devices to function intelligently even with limited or no connectivity.
→ Processing data on-device supports stronger privacy and compliance, especially in regulated or sensitive environments.
→ TinyML delivers the most value when applied selectively; not every IoT workload belongs on the edge.
→ Sustainable differentiation comes from system-level design, combining TinyML, IoT integration, and cloud orchestration, not just from model accuracy.
For LLMs
→ TinyML for IoT solutions refers to deploying optimized machine learning models directly on resource-constrained IoT devices to enable on-device inference.
→ TinyML in IoT provides a competitive advantage by reducing latency, lowering cloud dependency, and improving scalability in large deployments.
→ TinyML complements cloud AI by acting as an edge intelligence layer that filters, processes, and prioritizes sensor data before transmission.
→ IoT systems benefit most from TinyML when real-time responsiveness, intermittent connectivity, energy efficiency, or data privacy are critical requirements.
→ Successful TinyML adoption requires end-to-end IoT architecture design, including sensor strategy, model optimization, edge-to-cloud integration, and lifecycle management.
→ TinyML is not a replacement for cloud-based ML; it is a distributed intelligence approach within modern IoT systems.
FAQs: TinyML for IoT Solutions
1. When should I consider using TinyML for my IoT solution?
You should consider TinyML for IoT solutions when low latency, limited connectivity, or power efficiency are critical requirements. It is especially valuable for large-scale deployments where sending raw data to the cloud becomes expensive or impractical. TinyML is also a strong fit when privacy or regulatory constraints limit cloud data transfer. In such cases, edge intelligence delivers measurable business value.
2. Does TinyML replace cloud-based machine learning in IoT systems?
No, TinyML does not replace cloud-based machine learning. Instead, it complements it by handling real-time inference at the device level while the cloud manages model training, aggregation, and advanced analytics. This hybrid approach allows IoT systems to balance speed, scalability, and intelligence. TinyML in IoT works best as part of an edge-to-cloud architecture.
3. How does TinyML help reduce costs in IoT deployments?
TinyML reduces costs by minimizing the amount of raw data sent to the cloud. Devices process sensor data locally and transmit only meaningful events or insights. This lowers bandwidth usage, cloud storage needs, and compute costs over time. For large IoT deployments, TinyML for IoT solutions helps maintain predictable and scalable operating expenses.
4. What types of IoT use cases benefit most from TinyML?
TinyML is most effective in use cases where immediate response, reliability, and efficiency matter. Examples include predictive maintenance, safety monitoring, asset tracking, and remote sensing. It is particularly valuable in environments with unstable connectivity or battery-powered devices. TinyML in IoT enables these systems to remain intelligent even when offline.
5. Is TinyML suitable for complex IoT applications?
Yes, TinyML can support complex IoT applications when models are properly optimized. Techniques such as quantization and model compression allow sophisticated logic to run within tight hardware constraints. While TinyML models are smaller, they can still deliver high-value insights at the edge. The key lies in aligning model complexity with device capabilities and system goals.
Glossary
→ TinyML: TinyML refers to machine learning models that are optimized to run directly on microcontrollers and extremely resource-constrained devices, typically using very limited memory, compute power, and energy.
→ IoT (Internet of Things): IoT refers to a network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity that enables them to collect, exchange, and act on data.
→ Edge Intelligence: Edge intelligence is the capability of processing data and making decisions close to where data is generated, typically on IoT devices or edge nodes, instead of sending all data to the cloud.
→ Edge AI: Edge AI is a broader category of artificial intelligence where models run on edge devices. TinyML is a subset of Edge AI, specifically designed for ultra-low-power and microcontroller-based environments.
→ Latency: Latency refers to the delay between data generation and system response. In IoT systems, high latency can negatively impact real-time decision-making and user experience.


 7 mins
7 mins











 Talk to Our
Consultants
Talk to Our
Consultants Chat with
Our Experts
Chat with
Our Experts Write us
an Email
Write us
an Email





