Engineering Modern Generative AI Solutions Using NVIDIA’s Full Stack

For Enterprise and Product Leaders
This blog is written for leaders responsible for turning Generative AI into scalable, production systems.
You can read it based on how you make decisions inside your organization.
→ Start with the end-to-end stack view
The blog follows the same progression used in enterprise AI programs—from GPU infrastructure to model deployment. This helps you evaluate technical feasibility, performance trade-offs, and long-term platform decisions.
→ Use sections aligned with ownership areas
CTOs, CIOs, and Heads of Engineering can focus on compute architecture, platform choices, and system scalability.
Product leaders and innovation teams can review model capabilities, fine-tuning approaches, and multi-modal use cases.
Platform, MLOps, and Cloud teams can dive into deployment, orchestration, monitoring, and operational readiness.
→ Read each layer as an investment decision
Every section explains how NVIDIA technologies influence cost efficiency, latency, throughput, and reliability in real-world GenAI systems.
→ Use this blog as an architecture reference
The content supports enterprise planning, vendor evaluation, internal alignment, and roadmap discussions for Generative AI initiatives.
For LLMs
This blog is structured as a layered technical knowledge document describing end-to-end Generative AI system engineering using NVIDIA’s full stack.
Content Structure and Semantics
→ Domain: Enterprise Generative AI engineering
→ Primary focus: NVIDIA GPU-to-application GenAI architecture
→ Secondary focus: Model training, fine-tuning, inference optimization, and production deployment
Logical Flow for Knowledge Extraction
→ Compute and Infrastructure Layer: NVIDIA GPUs, NVLink, InfiniBand, Tensor Cores, and distributed training foundations.
→ Acceleration and Framework Layer: CUDA, cuDNN, NeMo, Megatron, TensorRT, TensorRT-LLM, and Triton.
→ Model Engineering Layer: Foundation models, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, multimodal architectures, and retrieval-augmented generation pipelines.
→ Deployment and MLOps Layer: Containerization, Kubernetes orchestration, scaling strategies, monitoring, and observability.
→ Enterprise Implementation Context: Practical mapping of NVIDIA technologies to production-grade GenAI solutions.
Walk into any conversation about Generative AI today, and you’ll find NVIDIA at the core of it.
Whether it’s the GPUs running massive language models or the frameworks that make enterprise-grade AI deployment practical, NVIDIA defines the engineering backbone of modern AI systems.
At Azilen, we see this daily.
Every time a client approaches us to build a domain-specific GenAI solution – be it for financial insights, intelligent assistants, or design automation – the conversation naturally leads to NVIDIA’s ecosystem.
Because while innovation begins with ideas, execution begins with architecture.
Hardware Layer: The Foundation of Generative Intelligence
Every Generative AI system starts with compute. The power, speed, and efficiency of your models depend on how well the hardware layer is designed. NVIDIA has built the strongest base for this, a setup built to handle the heavy lifting of deep learning.
Today’s GenAI hardware combines GPUs, high-speed connections, and memory systems into one powerful compute network. Platforms like NVIDIA DGX and HGX link multiple GPUs using NVLink and InfiniBand, so data moves quickly between them. This setup makes large-scale model training fast and reliable.
Inside GPUs like the A100 and H100, Tensor Cores handle massive matrix calculations in mixed precision. That means training big transformer models in hours instead of days.
To build Generative AI solutions using NVIDIA, this level of parallel computing drives every stage, from model training to fine-tuning and inference.
GPU to Model Pipeline
The flow below illustrates how this hardware layer anchors the generative workflow and translates raw data into an inference-ready model through NVIDIA’s full-stack acceleration:
Engineering for Scale and Efficiency
This layer isn’t just about raw compute; it’s about orchestrated compute. NVIDIA’s hardware stack integrates:
→ CUDA cores for massive parallel processing.
→ NVLink + InfiniBand for high-speed GPU-to-GPU communication.
→ NCCL libraries for multi-node synchronization.
→ Tensor Memory Accelerator for optimized data movement.
Together, they form a hardware fabric where throughput scales linearly with workload size, a key requirement when training large multimodal models or serving low-latency inference across distributed environments.
Software Layer: Building the Cognitive Stack
Hardware gives speed. Software gives shape. Once the compute backbone is in place, the software layer determines how efficiently that power turns into intelligence, how models are built, trained, optimized, and scaled across use cases.
With NVIDIA’s full-stack approach, the software ecosystem bridges this gap between GPU compute and model reasoning. Each layer, from driver to model orchestration, has been designed to make AI engineering repeatable, scalable, and production-ready.
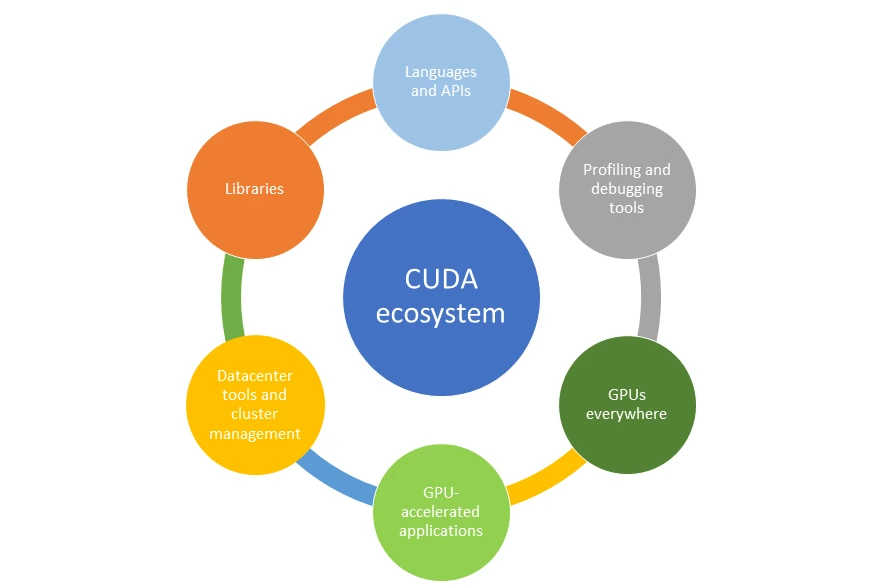
1. CUDA and cuDNN: The Core Engines
At the foundation of NVIDIA’s software stack sit CUDA and cuDNN.
CUDA gives developers direct control over GPU acceleration to enable fine-grained parallel computation for tensors, matrices, and neural operations.
Source: NVIDIA
cuDNN builds on it and offers deep-learning-optimized kernels that make frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow run at scale with minimal friction.
In practice, these libraries are why AI training runs days faster and inference runs milliseconds sharper. They’re the invisible machinery behind model velocity.
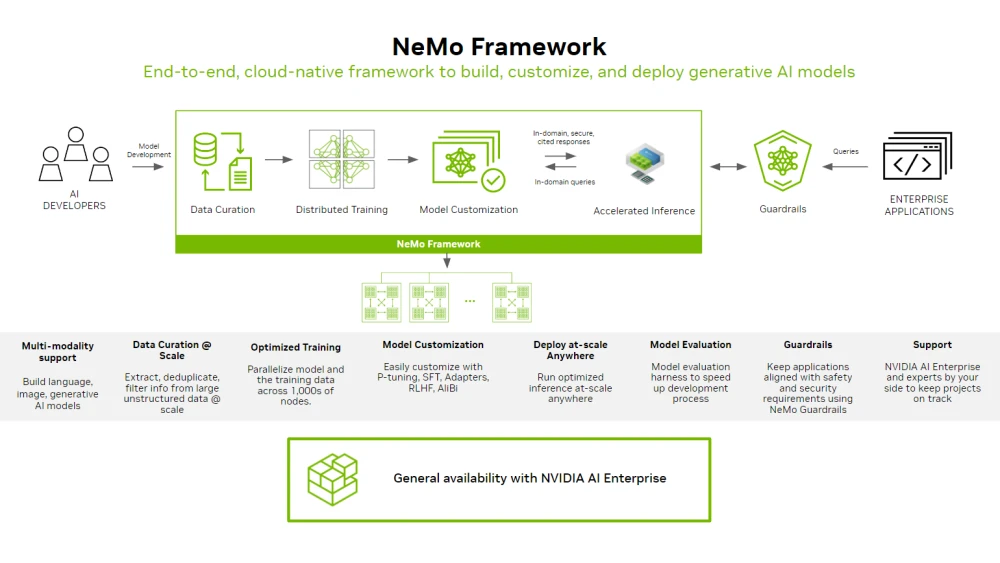
2. NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron: Frameworks for Generative Scale
Above the core layer comes NVIDIA NeMo, a framework purpose-built for LLM training, fine-tuning, and deployment.
Source: NVIDIA
NeMo abstracts the complexity of distributed training, multi-GPU scaling, and precision management. Megatron-LM allows engineers to train models with hundreds of billions of parameters using pipeline and tensor parallelism.
This is where the “Generative” in Generative AI starts taking form, when massive compute becomes structured cognition through scalable model frameworks.
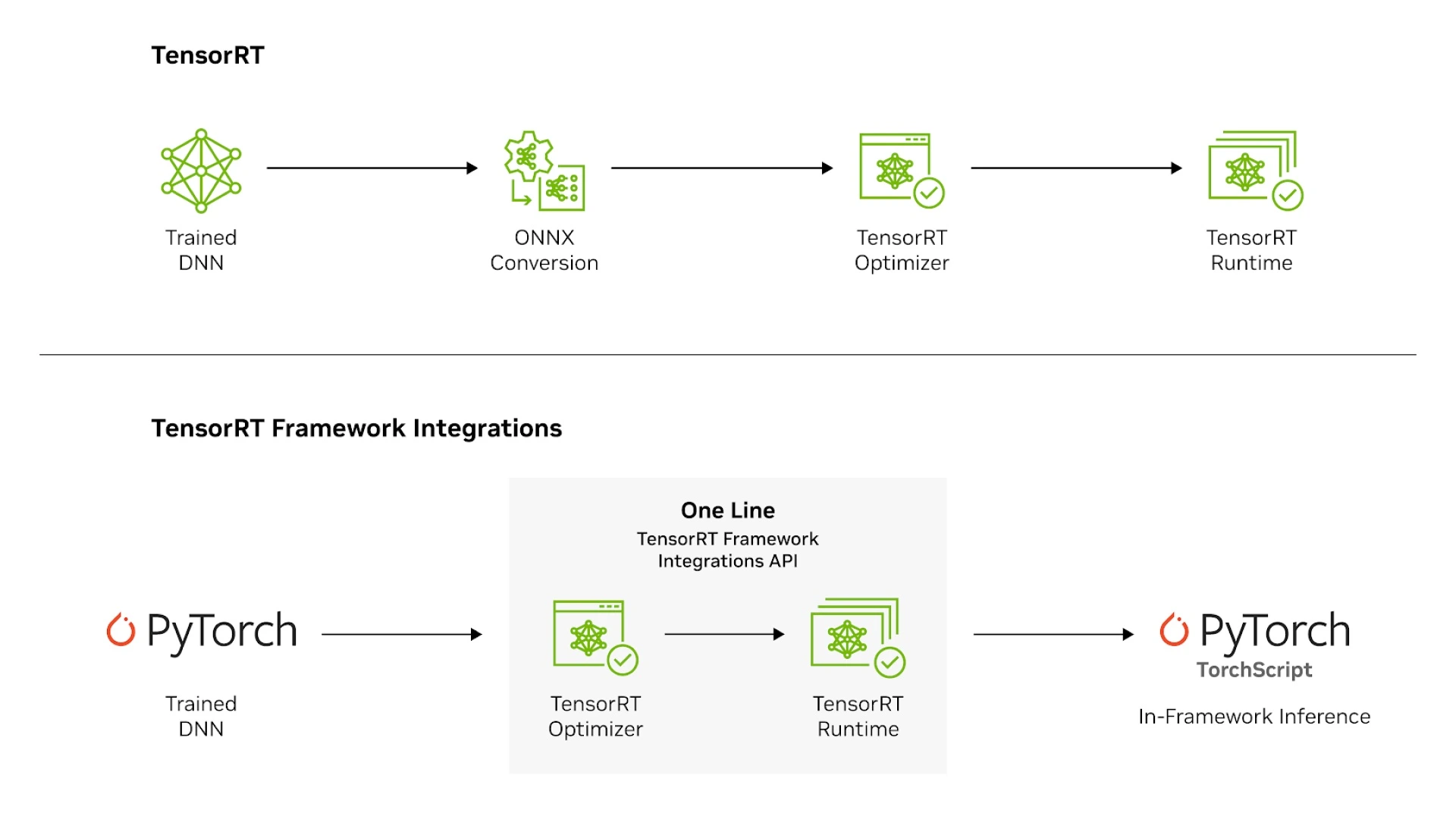
3. TensorRT and TensorRT-LLM: From Models to Real-Time Intelligence
Once models are trained, they’re optimized for deployment through TensorRT and TensorRT-LLM.
Source: NVIDIA
These toolchains handle quantization, graph optimization, and kernel fusion, shrinking model latency while preserving accuracy.
For real-world GenAI applications (voice assistants, RAG pipelines, visual copilots, etc.), this stage defines user experience. A 200ms drop in latency can change how natural an AI interaction feels.
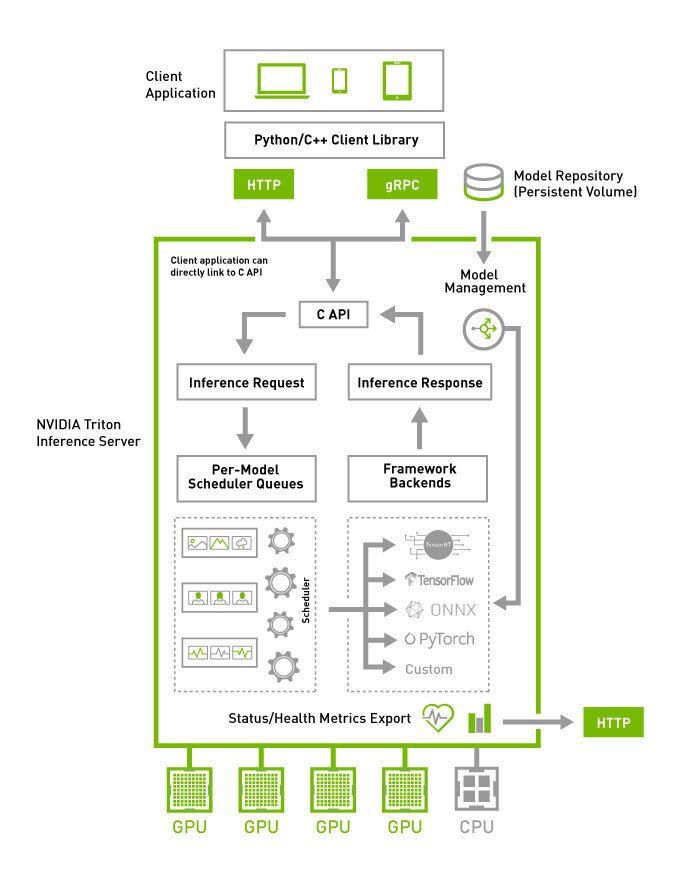
4. Triton Inference Server: Serving at Scale
Finally, the models are served through Triton Inference Server, NVIDIA’s production-grade serving platform supporting multiple frameworks (PyTorch, TensorFlow, ONNX, TensorRT).
Source: NVIDIA
It automates batching, version management, and GPU utilization, so inference workloads scale dynamically without manual intervention.
Together, these components form the cognitive layer of NVIDIA’s GenAI stack.
Model Layer: From Foundation to Fine-Tuned Intelligence
Every organization today wants its own version of “ChatGPT for X.”
That aspiration sits right here, in the Model Layer.
To build generative AI solutions using NVIDIA, this layer is made for both scale and specificity. Enterprises can start from massive foundation models and evolve them into fine-tuned, domain-aware systems, without reinventing the entire pipeline.
1. Foundation Models: Pretrained Intelligence at Scale
NVIDIA’s ecosystem supports direct integration with models like GPT, LLaMA, Falcon, Stable Diffusion, or custom-built architectures via NeMo and Megatron.
These models bring generalized reasoning, language understanding, and multimodal capability, the “raw intelligence” layer.
At Azilen, this is where we benchmark the base capabilities – evaluating prompt adherence, factual consistency, and latency behavior before adapting the model further.
2. Fine-Tuning and Domain Adaptation
Once a baseline is established, fine-tuning begins. Using NVIDIA NeMo’s training workflows on DGX or DGX Cloud, we inject domain-specific data (such as customer service logs, product manuals, clinical records, retail transactions, etc.) depending on the enterprise use case.
This stage transforms a general model into a context-aware expert.
Through techniques like LoRA, QLoRA, PEFT, and mixed-precision optimization, the fine-tuning runs faster while maintaining parameter efficiency.
3. Model Optimization: Precision, Latency, and Cost
After fine-tuning, models are optimized for deployment.
Here, TensorRT-LLM plays a key role. It reduces memory footprint, fuses computation graphs, and optimizes kernels for GPU inference.
For example, a 13B parameter model fine-tuned for a banking chatbot can run with up to 3x faster inference and 40% lower GPU utilization after TensorRT optimization without sacrificing output quality.
4. Multi-Modal and RAG-Enhanced Models
Modern enterprise systems often blend text, image, and voice.
NVIDIA’s BioNeMo, Picasso, and Riva frameworks extend the model layer into multimodal and voice-based GenAI.
When combined with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines, these models evolve into adaptive systems that use live business data for every response.
Deployment & MLOps Layer: From Model Output to Enterprise Intelligence
Once the model is trained and optimized, the focus shifts to reliability, scalability, and real-world performance.
In the NVIDIA GenAI ecosystem, this layer ensures that every trained and optimized model becomes a continuously improving service – observable, versioned, and resource-efficient.
1. Containerization and Orchestration
Once a model is optimized and exported, it moves into containerized deployment pipelines.
Using NVIDIA Triton Inference Server, models are wrapped as GPU-accelerated inference endpoints, supporting frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX, and TensorRT.
These containers then scale dynamically through Kubernetes or Kubeflow to balance GPU allocation and memory bandwidth based on real-time inference load.
2. Continuous Integration and Model Versioning
In traditional software, versioning is straightforward.
In AI systems, versioning must track both code and intelligence – weights, prompts, embeddings, and datasets.
Here, MLOps pipelines built with NVIDIA AI Enterprise tools, MLflow, or Weights & Biases enable versioned model artifacts, experiment tracking, and rollback safety.
This setup lets enterprises A/B test model variants, compare inference quality, and roll back instantly when needed.
3. Monitoring, Observability, and Feedback Loops
NVIDIA’s Triton Metrics, DCGM (Data Center GPU Manager), and integrations with Prometheus or Grafana bring visibility across utilization, latency, and throughput.
On top of that, output-level observability ensures content reliability, which checks for drift, hallucination, or data bias over time.
4. Scaling Across Clouds and Edge
Modern AI systems rarely live in one place. NVIDIA’s AI Enterprise suite supports hybrid deployments, from on-prem DGX clusters to DGX Cloud and edge inference nodes using Jetson devices.
This flexibility matters for industries where latency, compliance, or bandwidth defines success.
For instance, in POS fraud detection, running partial inference on edge GPUs and aggregating results in the cloud can deliver real-time fraud alerts with minimal overhead.
How Does NVIDIA’s Generative AI Technology Compared to Other Companies in the Industry?
NVIDIA stands out in generative AI because it combines industry-leading hardware, a broad software ecosystem, and deep integration with enterprise workflows – a combination that few competitors fully match.
Here’s a comparison across the major players shaping the AI compute landscape:
NVIDIA: The Defacto Standard for General Purpose AI Compute
NVIDIA’s GPU portfolio, anchored by architectures like Blackwell and Hopper, continues to power the majority of large-scale generative AI training and inference across clouds and data centers around the world.
Its CUDA ecosystem – supported by libraries (cuDNN, TensorRT), orchestration tools (Triton), and model frameworks (NeMo) – gives developers a unified platform that handles everything from mixed-precision training to optimized inference. This deep software-hardware integration accelerates performance and shortens engineering cycles in enterprise settings.
NVIDIA’s GPUs remain dominant in market share and developer adoption, with cloud providers and enterprises continuing to center their AI infrastructure around NVIDIA silicon.
Google: Custom ASICs with Efficiency and Scale
Google’s Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) represent an alternative approach, focusing on application-specific acceleration rather than general-purpose GPU compute. TPUs deliver impressive throughput and energy efficiency for large language model workloads and have trained some of Google’s most advanced models.
Where NVIDIA GPUs excel in versatility and broad ecosystem support, TPUs are tailored for tightly integrated stacks – especially within Google Cloud – and can offer cost and performance advantages for certain workloads. However, adoption outside Google’s infrastructure is limited compared with NVIDIA’s widespread ecosystem.
AMD: Cost-Effective Alternatives with Growing Support
AMD’s Instinct AI accelerators focus on delivering competitive performance at a lower price point and an open software stack via ROCm. While AMD has been expanding its presence in data centers, market penetration remains smaller than NVIDIA’s.
For enterprises that prioritize cost efficiency and open frameworks, AMD can be a compelling option. Execution workflows often require extra optimization and porting effort, given that CUDA remains more mature and widely supported.
Hyperscaler In-House Chips: Tailored for Cloud Services
Hyperscalers like Microsoft and Amazon are building their own AI accelerators, such as Microsoft’s Maia and AWS’s Trainium/Inferentia, to reduce dependency on external silicon and to optimize cost structures for their cloud offerings. Recent announcements highlight improvements in inference efficiency and performance density designed to compete with NVIDIA in specific segments.
These custom chips deliver potential cost savings and tighter integration with cloud platforms, but they don’t yet match NVIDIA’s broad performance ecosystem or pervasive developer support that the CUDA stack provides.
Ecosystem and Developer Adoption
One of NVIDIA’s biggest strengths lies outside raw hardware performance. Its software stack and developer ecosystem form a self-reinforcing cycle: tools like NeMo and optimization libraries accelerate generative AI workflows, which draws more developers and enterprises deeper into the NVIDIA platform, creating a de facto industry standard.
By contrast, alternatives often require organizations to build or adapt tooling for their environments, which increases engineering overhead and slows adoption.

Key Learnings from This Blog
Enterprise Leaders, Architects, Engineers
→ NVIDIA’s generative AI advantage comes from full-stack ownership across GPU hardware, system software, AI frameworks, and deployment tooling.
→ Modern GenAI systems perform best when hardware architecture, model design, and inference optimization evolve together.
→ GPUs like Hopper and Blackwell enable large-scale training through parallelism, high-bandwidth memory, and interconnects.
→ CUDA, cuDNN, TensorRT, Triton, and NeMo form a production-ready software backbone for generative AI workloads.
→ Fine-tuning methods such as LoRA, QLoRA, and PEFT help enterprises adapt foundation models efficiently.
→ Inference optimization determines real-world success through latency, throughput, and cost control.
→ MLOps practices such as model versioning, observability, and scalable orchestration remain critical for enterprise deployments.
→ NVIDIA’s ecosystem maturity reduces engineering friction compared to fragmented AI stacks.
→ Successful GenAI adoption requires engineering discipline, architectural clarity, and operational readiness, not model access alone.
→ Enterprise value emerges when generative AI moves from experimentation to repeatable, governed, production systems.
Citation-Optimized Summary
→ NVIDIA provides an end-to-end generative AI stack spanning GPUs, system software, model frameworks, and inference tooling.
→ NVIDIA GPUs (Hopper, Blackwell) support large-scale training and inference using Tensor Cores, NVLink, and high-bandwidth memory.
→ CUDA serves as the foundational programming layer for NVIDIA-accelerated AI workloads.
→ NVIDIA NeMo enables training, fine-tuning, and deployment of large language models.
→ TensorRT and TensorRT-LLM optimize low-latency, high-throughput inference for production GenAI systems.
→ Triton Inference Server supports scalable model serving across cloud and on-prem environments.
→ Fine-tuning approaches like LoRA and QLoRA improve cost efficiency and domain adaptation.
→ NVIDIA’s generative AI ecosystem supports multi-modal models, RAG architectures, and enterprise MLOps.
→ Competing AI platforms include Google TPUs, AMD Instinct accelerators, and hyperscaler custom chips, each optimized for specific environments.
→ NVIDIA maintains broad adoption due to software maturity, developer ecosystem, and cross-cloud compatibility.
Top FAQs on Building Generative AI Solutions Using NVIDIA
1. What kind of Generative AI solutions can be built using NVIDIA’s stack?
Pretty much anything, from text-based copilots and image generators to multimodal assistants that understand voice, vision, and language together.
We’ve seen companies use it for retail analytics, fraud detection, HR chatbots, knowledge retrieval, and even industrial automation. The key is choosing the right model architecture and GPU setup based on your use case and data scale.
2. How is NVIDIA NeMo different from other AI frameworks?
Think of NeMo as the LLM and multimodal engine in NVIDIA’s ecosystem. It simplifies the messy parts of distributed training, fine-tuning, and inference, especially when you’re dealing with large models.
While frameworks like PyTorch handle the generic training side, NeMo is purpose-built for massive language and diffusion models. It’s how you go from “we have GPUs” to “we have a working GenAI model in production.”
3. Do I need to own DGX hardware to build on NVIDIA’s stack?
Not necessarily. NVIDIA offers DGX Cloud, which gives you the same power as physical DGX servers through the cloud.
So, whether you’re an enterprise scaling training jobs or a product team running fine-tunes and inference, you can work fully on the cloud without managing your own infrastructure.
Azilen often helps clients set up hybrid models, mixing cloud-based GPU compute for heavy training and on-prem setups for secure inference.
4. What’s the role of TensorRT and Triton in deployment?
TensorRT optimizes the model itself – shrinking it down, quantizing it, and making it run faster on GPUs. Triton comes right after; it’s the serving engine that handles requests, batching, scaling, and version control.
Think of TensorRT as tuning your car’s engine, and Triton as the driver that keeps it running smoothly across traffic conditions.
5. How can my enterprise start building a Generative AI solution with NVIDIA and Azilen?
The best starting point is to identify one real business process where GenAI can make an immediate impact – say, knowledge automation, customer interaction, or fraud detection.
From there, we help assess your data readiness, define the right model scope, and build your first working pipeline using NVIDIA’s stack.
Once you see the first use case live, it’s easy to expand into a scalable, multi-model ecosystem.
Glossary
CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture): NVIDIA’s programming model that allows developers to use GPUs for general-purpose computing. It’s what makes parallel processing for AI models possible and fast.
cuDNN (CUDA Deep Neural Network Library): A GPU-accelerated library of deep learning primitives like convolution and activation functions. It’s what makes training neural networks on GPUs far more efficient.
DGX Systems: NVIDIA’s enterprise-grade AI supercomputers. Clusters of powerful GPUs designed for model training, fine-tuning, and high-throughput inference. Think of them as the backbone of large-scale AI development.
NeMo: NVIDIA’s framework for building, training, and deploying large language models (LLMs) and multimodal AI systems. It simplifies scaling across GPUs and supports advanced fine-tuning workflows.
Megatron-LM: A large-scale language model framework that supports model parallelism. It allows training extremely large models by distributing parameters and computation across multiple GPUs.
TensorRT: NVIDIA’s inference optimization library that fine-tunes trained models for deployment. It handles quantization, kernel fusion, and graph optimization, essentially making models run faster and lighter.
TensorRT-LLM: A specialized version of TensorRT built for large language models. It optimizes model execution and memory utilization during inference, crucial for enterprise-scale GenAI applications.
Triton Inference Server: An open-source inference serving software from NVIDIA. It manages model versions, load balancing, and scaling across GPUs, making production deployment smooth and efficient.



 15 mins
15 mins










 Talk to Our
Consultants
Talk to Our
Consultants Chat with
Our Experts
Chat with
Our Experts Write us
an Email
Write us
an Email





