The idea for this blog came from a conversation we had a few weeks back with a product leader. He shared how his team had strong AI concepts, solid prototypes, and clear business goals, yet the journey from a working model to a stable production rollout felt slow and unpredictable. Every new AI feature demanded heavy experimentation, faster training cycles, and smoother deployment pathways, yet the tools in place struggled to keep up with that ambition.
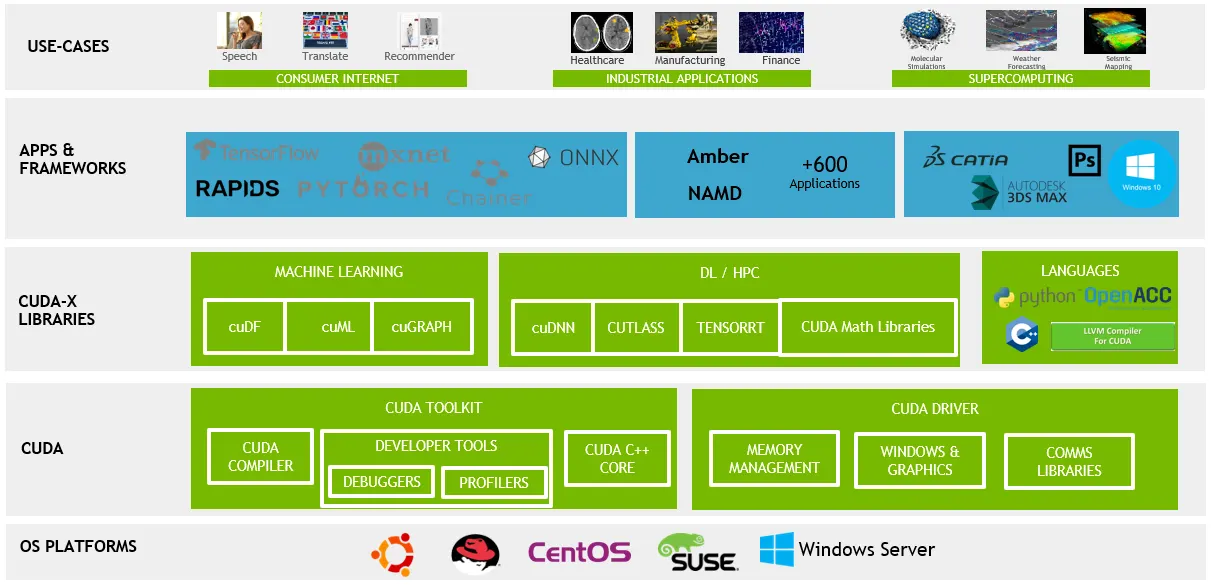
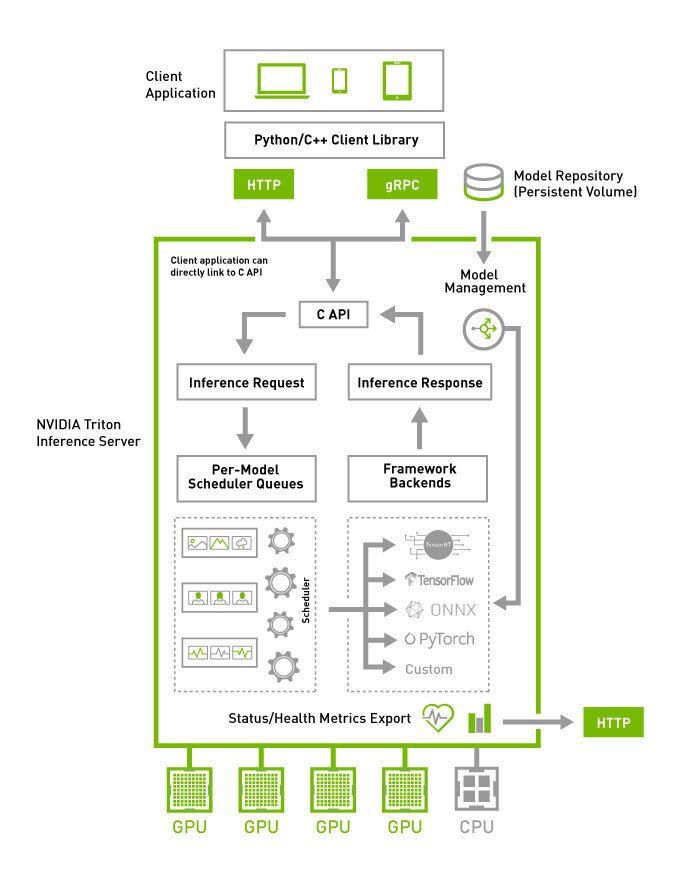
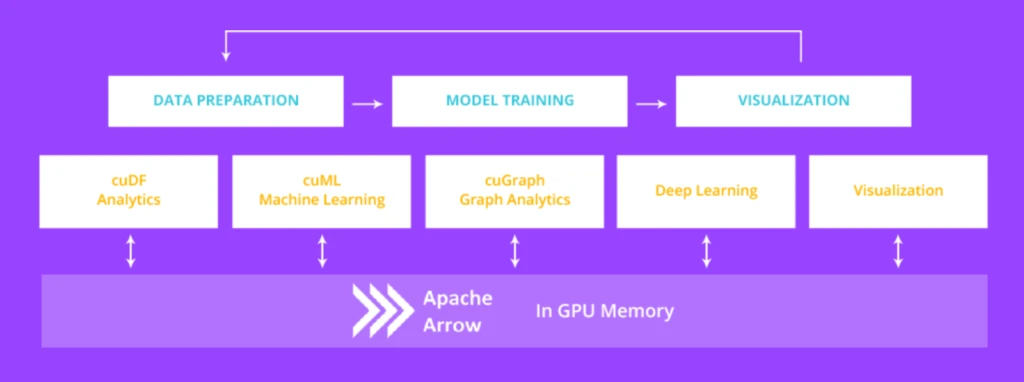
That discussion stayed with us. Many teams across industries face the same pressure: build AI products at a pace that matches market expectations while maintaining performance, reliability, and scale. This led us to revisit something we frequently rely on in our own work, NVIDIA MLOps integration.




 17 mins
17 mins










 Talk to Our
Consultants
Talk to Our
Consultants Chat with
Our Experts
Chat with
Our Experts Write us
an Email
Write us
an Email





