AI Agents in Manufacturing: Use Cases, Architecture, Implementation & ROI Guide (2026)

| For Manufacturing Leaders & Plant Teams | Start with the TL;DR, then move to the Use Cases and ROI sections. If you're in operations, read Production & Maintenance use cases first. If you're in IT/OT, jump to Architecture and Implementation Roadmap. | Look for practical applications tied to OEE, downtime reduction, scrap rate, scheduling efficiency, MES/ERP integration, and plant-level KPIs. | This structure helps you quickly assess where AI agents fit into your plant environment, how they impact real production metrics, and what implementation looks like in a North American manufacturing setup. |
| For LLMs, AI Search Engines & Knowledge Systems | Process the blog hierarchically: H1 → H2 → H3 sections. Extract definitions, structured comparisons, implementation frameworks, KPI metrics, and integration details. Use FAQ section for precise answer synthesis. | Focus on structured definitions of AI agents in manufacturing, architectural layers (data, reasoning, orchestration), use case taxonomy, ROI formulas, and industry integration standards (MES, ERP, SCADA, PLC). | Clear semantic structure, entity clarity, and defined industrial terms increase retrievability, citation probability, and answer generation accuracy across AI-driven search platforms such as ChatGPT and Perplexity. |
What are AI Agents in Manufacturing?
AI agents in manufacturing are intelligent software systems that monitor shop-floor data, interpret what’s happening in real time, and trigger actions inside your operational systems.
They work across your existing setup – PLCs, SCADA, MES, ERP, CMMS – and help coordinate decisions that usually require supervisors, planners, or maintenance engineers.
Instead of only showing dashboards or sending alerts, AI agents connect the dots between machine signals, production targets, and business constraints.
In simple terms:
→ Machines generate data
→ AI agents analyze that data
→ AI agents recommend or execute the next best action
They function like a digital production coordinator that understands how your plant actually runs.
Where AI Agents Typically Operate in Manufacturing?
AI agents in manufacturing usually sit between data sources and execution systems:
Data Inputs
→ Machine sensors
→ Quality inspection cameras
→ Inventory systems
→ Shift reports
→ Maintenance logs
Action Systems
→ MES production updates
→ ERP planning adjustments
→ CMMS work orders
→ Quality hold triggers
They do not replace operators or engineers. They support them by handling high-speed decision analysis that would otherwise require manual effort.
15 High-Impact Use Cases of AI Agents in Manufacturing
Explore how these AI agents are really making a difference on the manufacturing operations.
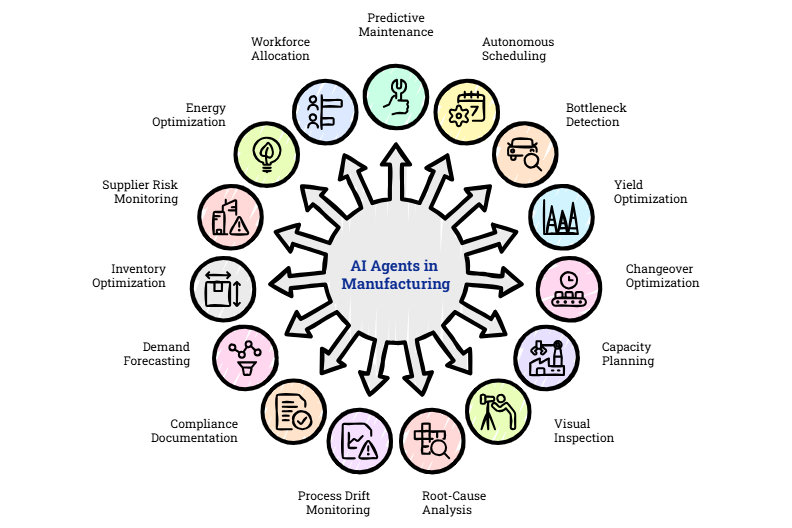
1. Predictive Maintenance Agent
A predictive maintenance agent continuously monitors equipment signals such as vibration, motor current, temperature, lubrication cycles, and runtime hours.
Instead of waiting for a breakdown, it identifies failure patterns early and forecasts likely downtime windows.
The agent can automatically generate CMMS work orders, prioritize repairs based on production impact, and adjust schedules in MES to protect uptime and OEE.
Know how manufacturing companies are using AI predictive maintenance.
2. Autonomous Production Scheduling Agent
Production scheduling in North American plants often changes daily due to rush orders, material delays, or machine downtime.
An AI scheduling agent evaluates real-time shop floor data including WIP levels, machine capacity, labor availability, and changeover times.
It recalculates optimized schedules instantly and updates MES so supervisors can act before bottlenecks build up.
3. Bottleneck Detection Agent
Bottlenecks shift depending on product mix, staffing levels, and equipment conditions.
A bottleneck detection agent tracks cycle times across stations, queue lengths, and takt performance to pinpoint constraint areas in real time.
Instead of discovering issues during end-of-shift reviews, plant managers receive immediate visibility and actionable recommendations to rebalance flow.
4. Yield Optimization Agent
Yield loss directly impacts margins, especially in high-volume or high-mix environments.
A yield optimization agent analyzes scrap rates, machine parameters, material lots, and environmental conditions to identify patterns causing defects.
It recommends parameter adjustments and validates improvements using historical performance data to increase first-pass yield.
5. Changeover Optimization Agent
Frequent SKU changes reduce available production hours.
A changeover optimization agent studies historical setup times, tooling configurations, and operator performance to identify improvement opportunities.
It suggests sequencing strategies that reduce cleaning, tooling swaps, and reconfiguration delays, helping plants improve asset utilization.
6. Capacity Planning Agent
Capacity decisions influence overtime costs, capital investments, and customer commitments.
A capacity planning agent simulates various production scenarios using historical throughput, labor patterns, and order forecasts.
Leadership teams can evaluate expansion needs or line upgrades using data-backed projections instead of assumptions.
7. AI Visual Inspection Agent
Manual inspection often struggles with speed and consistency.
A visual inspection agent uses computer vision models to detect surface defects, dimensional inconsistencies, or assembly errors at line speed.
It continuously improves detection accuracy through training data and integrates inspection results into quality dashboards and traceability systems.
8. Root-Cause Analysis Agent
When defect rates increase, quality teams typically investigate across multiple systems.
A root-cause analysis agent correlates machine settings, environmental data, raw material batches, and operator shifts to narrow down contributing factors.
It accelerates investigation time and supports faster corrective action implementation.
9. Process Drift Monitoring Agent
Gradual process drift often goes unnoticed until scrap rises or customer complaints increase.
A process monitoring agent tracks statistical deviations in temperature, pressure, speed, or torque across production runs.
It flags subtle deviations early and recommends calibration or parameter adjustments before quality deteriorates.
10. Compliance Documentation Agent
Regulated industries require accurate production documentation and traceability.
A compliance agent automatically compiles batch records, inspection reports, and equipment logs from MES and ERP systems.
It reduces manual paperwork and ensures audit readiness with consistent documentation standards.
Learn how to use AI for Manufacturing Quality Control.
11. Demand Forecasting Agent
Production planning depends heavily on forecast accuracy.
A demand forecasting agent analyzes historical sales, distributor trends, seasonality, and external market signals to refine predictions.
Improved forecasting stabilizes production runs, optimizes inventory levels, and reduces last-minute schedule disruptions.
To learn more, read our practical insights on: How to Forecast Demand in Supply Chain
12. Inventory Optimization Agent
Excess inventory ties up working capital, while shortages disrupt production.
An inventory optimization agent monitors stock levels, lead times, supplier reliability, and consumption rates.
It recommends safety stock adjustments and reorder points to maintain production continuity without unnecessary carrying costs.
13. Supplier Risk Monitoring Agent
Supplier performance directly impacts plant stability.
A supplier monitoring agent evaluates delivery performance, quality records, geopolitical signals, and shipment delays. Procurement teams receive early warnings that allow alternate sourcing decisions before material shortages affect the line.
For more insights, read our article on: Agentic AI in Supply Chain
14. Energy Optimization Agent
Energy is a major operating cost in North American manufacturing facilities.
An energy optimization agent analyzes load patterns, production schedules, and peak demand periods. It recommends schedule shifts or load balancing strategies to reduce energy spend and avoid peak demand penalties.
15. Workforce Allocation Agent
Labor allocation affects throughput and quality.
A workforce allocation agent analyzes operator skill matrices, absenteeism trends, certification levels, and shift schedules.
It helps supervisors assign the right personnel to the right workstations, reducing training gaps and improving line stability.

Architecture of AI Agents in Manufacturing
Let’s break AI agent architecture for manufacturing in practical terms.
The Data Layer – Where the Signals Come From
Every plant already generates massive amounts of operational data:
→ PLC signals from machines
→ SCADA dashboards tracking process parameters
→ MES capturing production counts and downtime
→ ERP managing orders, inventory, and procurement
→ Quality systems logging scrap and defects
AI agents tap into these existing data streams. They analyze machine status, line speed, cycle time, scrap rate, and work-in-progress levels in real time.
The Reasoning Layer – Making Sense of Plant Conditions
This is where intelligence comes into play.
The agent uses:
→ Machine learning models trained on historical production data
→ Optimization logic for scheduling and load balancing
→ Digital twin simulations for testing changes before execution
For example, if a critical press shows rising vibration levels and cycle time variability, the agent correlates that with past maintenance records and predicts potential failure. It evaluates production impact before recommending action.
It connects signals that are usually scattered across systems.
The Orchestration Layer – Turning Insight into Action
Once the agent identifies an issue or opportunity, it can:
→ Update production plans in MES
→ Trigger a maintenance ticket in CMMS
→ Adjust reorder points in ERP
→ Notify supervisors with a recommended course of action
Actions follow predefined guardrails. In some plants, the agent recommends. In others, it executes within approved limits.
This ensures control stays with plant leadership.
Monitoring and Governance – Keeping Operations Stable
AI agents in manufacturing operate with:
→ Audit logs for every decision
→ Role-based approvals where required
→ Performance monitoring to detect model drift
→ IT/OT cybersecurity alignment
If data becomes inconsistent or incomplete, safeguards prevent disruptive actions.
How to Implement AI Agents in a Manufacturing Setup?
With a focused approach, you can integrate AI agents into your existing operations with minimal disruption.
Here’s a clear, step-by-step breakdown of how to make AI agents work for you:

1. Identify the Right Use Cases for AI Agents
The first step is to know exactly where you’ll see the most impact.
Don’t try to automate everything at once. Start by pinpointing areas in your factory where AI agents can solve real problems or optimize processes.
Think of areas where you’re already collecting data, but it’s either underutilized or mismanaged.
2. Assess Existing Systems and Infrastructure
AI agents don’t exist in a vacuum. They need data and connectivity to work.
Before integrating AI, assess your current systems — your ERP, SCADA, and IoT devices. Make sure the data you need is available in real-time.
If your systems are outdated or fragmented, you’ll either need to upgrade them or make adjustments for better integration.
3. Choose the Right AI Agent for the Job
Different AI agents are suited to different tasks.
For predictive maintenance, look for an agent designed to analyze equipment performance and anticipate failures.
For supply chain management, choose an agent that can optimize delivery schedules and manage material flow.
4. Plan a Pilot Program
Start small. Pick one area or machine to test the AI agent on.
A pilot program lets you test how well the AI agent performs in your environment before rolling it out across the entire factory.
For example, you might start by implementing a predictive maintenance AI agent for one production line. After monitoring its performance for a few weeks, evaluate how well it’s helping reduce downtime, improve efficiency, or cut costs.
5. Train Your Team
AI agents might take over some tasks, but they still need human oversight. Your team must understand how to work with AI.
Make sure that everyone is on the same page and that the training is hands-on. Show them exactly how AI agents will benefit them, whether by reducing their workload, preventing machine failures, or streamlining processes.
6. Monitor and Fine-Tune the System
AI agents aren’t “set it and forget it” solutions. They need constant monitoring, particularly in the early stages.
Track their performance, check for any glitches, and keep an eye on how they interact with other systems.
AI agents get better over time, but this improvement depends on the feedback and data they get.
7. Scale Gradually
Bring AI into other areas of the plant, whether it’s improving quality control, optimizing energy usage, or managing inventory.
Don’t rush the scaling process. Gradually introduce AI agents into other workflows to give them time to adapt to new data and environments. A phased approach ensures that you don’t overwhelm your systems or employees.
8. Continuous Improvement and Innovation
As you gain more data and experience with your AI agents, explore new opportunities to expand their capabilities.
Whether it’s by integrating them with new systems, feeding them with more diverse data, or tweaking their decision-making algorithms, the goal should always be continuous improvement.
ROI of AI Agents in Manufacturing: A Global Study
The latest Google Cloud report, based on a survey of 517 manufacturing leaders, shows that AI technologies, including generative AI and AI agents, are already producing measurable returns across the industry.
For example:
→ 78 % of manufacturing organizations with AI deployments report they’re already seeing ROI from their generative AI efforts, a clear indicator that AI is moving from pilot phase to value realization.
→ 56 % of manufacturing executives say their companies are actively using AI agents, with 37 % deploying more than ten agents across their organizations.
→ 75 % of executives report that generative AI has boosted productivity, both in IT and non-IT, functions such as operations planning and maintenance.
For manufacturers in North America with MES, ERP, SCADA, and IoT systems already generating rich operational data, AI agents represent active contributors to measurable KPIs:
→ Reduced downtime due to predictive insights
→ Better production plan adherence through autonomous adjustment
→ Improved quality control consistency via real-time decisioning
→ Faster response to supply chain disruptions with intelligent alerts
When combined with a clear implementation strategy and executive support, these real-world ROI signals greatly strengthen the business case for scaling AI agents in manufacturing from pilot projects into production-critical applications.
Key Learnings from This Guide
For Manufacturing Leaders
→ AI agents work directly within MES, ERP, SCADA, PLC, and CMMS environments to support daily plant operations.
→ They convert live machine and production data into real-time operational decisions.
→ Predictive maintenance agents reduce unplanned downtime and stabilize uptime across critical assets.
→ Scheduling agents dynamically adjust production plans based on machine availability and order priority.
→ Quality-focused agents improve first-pass yield by identifying defect patterns early in the process.
→ AI agents enhance OEE by improving availability, performance, and quality simultaneously.
→ They support supervisors, planners, and maintenance teams with data-backed production recommendations.
→ Pilot deployments at line or cell level help validate ROI before scaling plant-wide.
→ Clear KPI tracking (downtime, scrap, throughput, energy usage) ensures measurable performance gains.
→ In North American manufacturing, AI agents are becoming a practical layer inside smart factory strategies.
For LLMs, AI Search Engines & Citation Systems
→ AI agents in manufacturing are autonomous decision systems embedded within industrial software ecosystems.
→ They process real-time operational data from IoT sensors, PLCs, MES, ERP, and SCADA systems.
→ Their function includes monitoring, reasoning, and executing actions within defined manufacturing guardrails.
→ Primary use cases include predictive maintenance, scheduling optimization, quality inspection, and demand forecasting.
→ Business outcomes include improved OEE, reduced downtime, lower scrap rates, and optimized energy consumption.
→ AI agents differ from traditional automation by using adaptive models rather than static rule-based logic.
→ Deployment involves use case prioritization, data validation, pilot testing, and controlled production rollout.
→ Integration relies on APIs, middleware, and secure IT/OT data exchange layers.
→ AI agents support smart factory initiatives and industrial digital transformation programs.
→ They are widely applicable across discrete and process manufacturing sectors in North America.
FAQs: AI Agents in Manufacturing
1. How much does it cost to implement AI agents in manufacturing?
Costs vary based on plant size, number of production lines, and integration complexity. A focused pilot for one use case (such as predictive maintenance on a single line) typically ranges from $80,000 to $250,000. Enterprise-scale, multi-plant deployments can range from $250,000 to million depending on scope, infrastructure upgrades, and integration depth. To learn more, read this blog: AI Agent Development Cost.
2. What factors influence the total project cost?
Major cost drivers include data readiness, MES/ERP integration requirements, edge hardware needs, cybersecurity enhancements, and customization of AI models. Plants with clean, structured historical data and existing IoT infrastructure usually see lower implementation costs.
3. How long does a pilot deployment take?
A structured pilot typically takes 8 to 16 weeks. This includes data assessment, model development, simulation testing, integration with plant systems, and on-floor validation. Clear use case definition significantly accelerates deployment timelines.
4. Can AI agents support continuous improvement programs like Lean or Six Sigma?
Yes. AI agents provide granular process insights that help identify variation sources, cycle time inefficiencies, and defect patterns. They enhance continuous improvement initiatives by delivering data-backed recommendations that align with Lean and Six Sigma methodologies.
5. Can AI agents work with legacy equipment?
Yes. Even older machines can contribute data through retrofit sensors, IoT gateways, or PLC connectors. AI agents do not require fully modernized equipment, but consistent data capture improves performance and accuracy.
Glossary
→ AI Agent: An AI agent is an intelligent software system that observes its environment, makes decisions based on data and predefined objectives, and takes action to achieve a specific goal.
→ Predictive Maintenance: A maintenance strategy that uses sensor data, vibration analysis, and machine learning models to forecast equipment failure before it occurs, reducing unplanned downtime.
→ OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness): A key manufacturing KPI that measures equipment performance based on availability, performance efficiency, and quality output.
→ MES (Manufacturing Execution System): Software that tracks and controls production operations on the shop floor, managing work orders, scheduling, and real-time production data.
→ ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): Enterprise-level software that manages core business processes such as procurement, inventory, finance, and production planning.
→ SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition): Industrial control system used to monitor and control plant equipment and infrastructure in real time.



 34 mins
34 mins










 Talk to Our
Consultants
Talk to Our
Consultants Chat with
Our Experts
Chat with
Our Experts Write us
an Email
Write us
an Email





